-
Inside Webster’s Lab: Removing Domain Controller Using PowerShell
December 31, 2014
With all the writing I do for my website and customers, I recreate my Windows Server 2012 R2 Active Directory (AD) environment frequently. Sometimes I just need a fresh start and I need to demote my domain controller, remove all the Active Directory related Roles and Features and just start over. This article will show how I use PowerShell to accomplish these tasks.
Start a PowerShell session and enter the following cmdlet.
Uninstall-ADDSDomainController ` -DemoteOperationMasterRole:$true ` -IgnoreLastDnsServerForZone:$true ` -LastDomainControllerInDomain:$true ` -RemoveDnsDelegation:$true ` -RemoveApplicationPartitions:$true ` -Force:$true
You will be prompted to enter and confirm the new local administrator password, as shown in Figure 1, and the removal process begins.
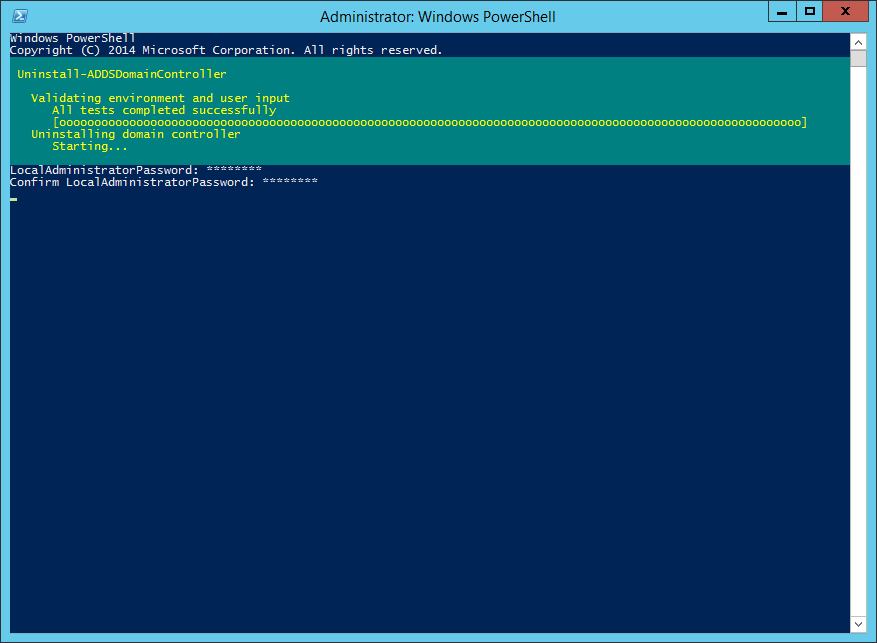
Figure 1 When the removal process is completed, as shown in Figure 2, the server will automatically restart.
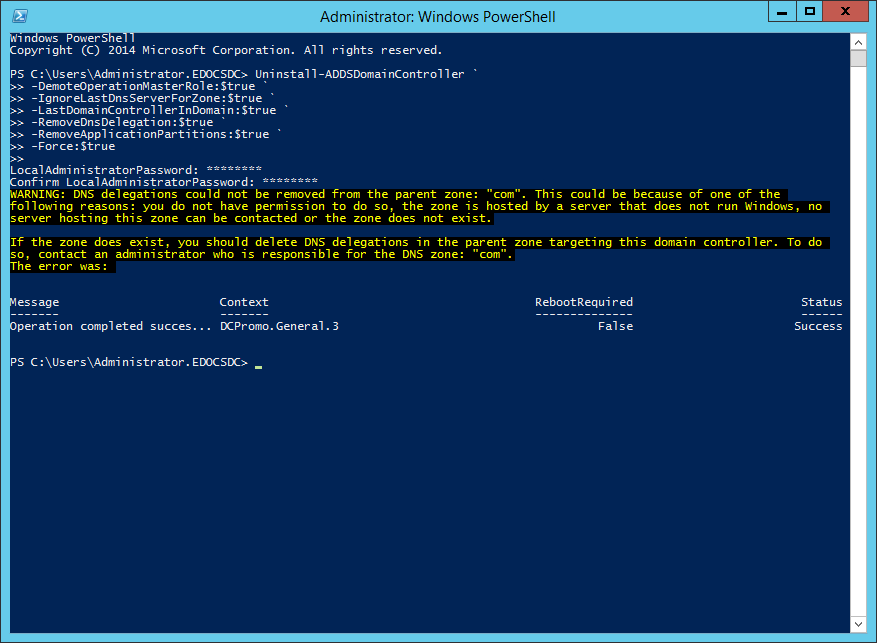
Figure 2 After the server restarts, log back into the server and start a PowerShell session.
Enter the following PowerShell cmdlets.
Uninstall-WindowsFeature -Name "ad-domain-services" -IncludeManagementTools Uninstall-WindowsFeature "RSAT-AD-Tools" Uninstall-WindowsFeature -Name "dns" -IncludeManagementTools Uninstall-WindowsFeature -Name "gpmc" -IncludeManagementTools
The results are shown in Figure 3.
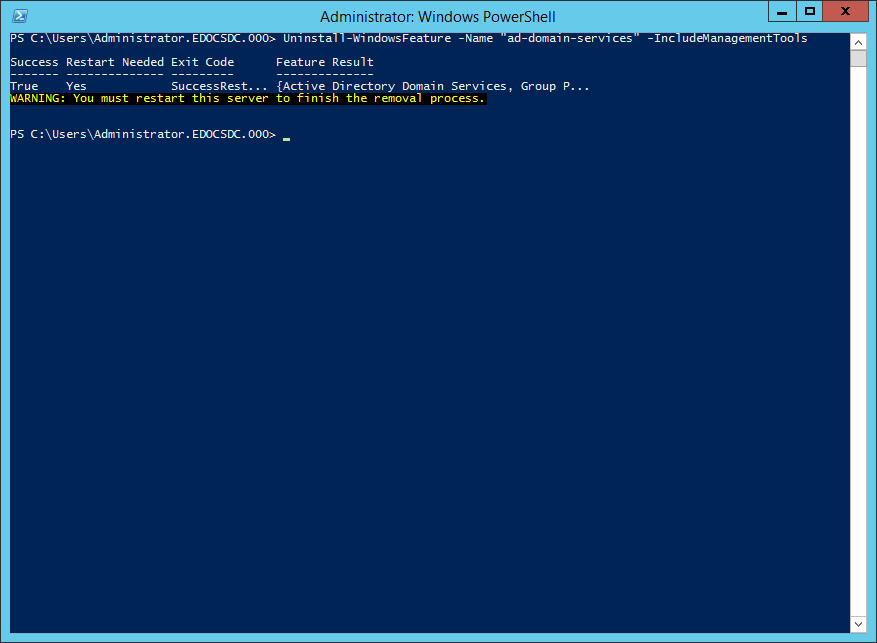
Figure 3 Restart the server to finish the removal process.
After the server restarts, log back into the server and click Tools on the Server Manager console. Figure 4 shows all the Active Directory, DNS, and Group Policy management tools are no longer installed.
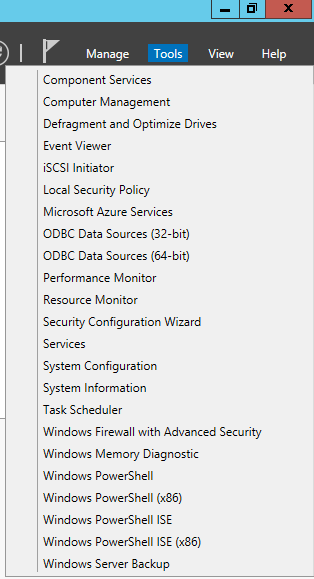
Figure 4 Now you are ready to start fresh with the server.
Using PowerShell for the domain controller removal process is much faster, in my opinion, than attempting to remove the ADDS Role and following the wizard to demote the domain controller.
Thanks
Webster
One Response to “Inside Webster’s Lab: Removing Domain Controller Using PowerShell”
Leave a Reply






May 5, 2021 at 1:28 am
Excellent script! Gets working without any issues!